What is a Cloud
What is a Cloud? What are the benefits of using a Cloud Provider? Read on to know more….
Definition
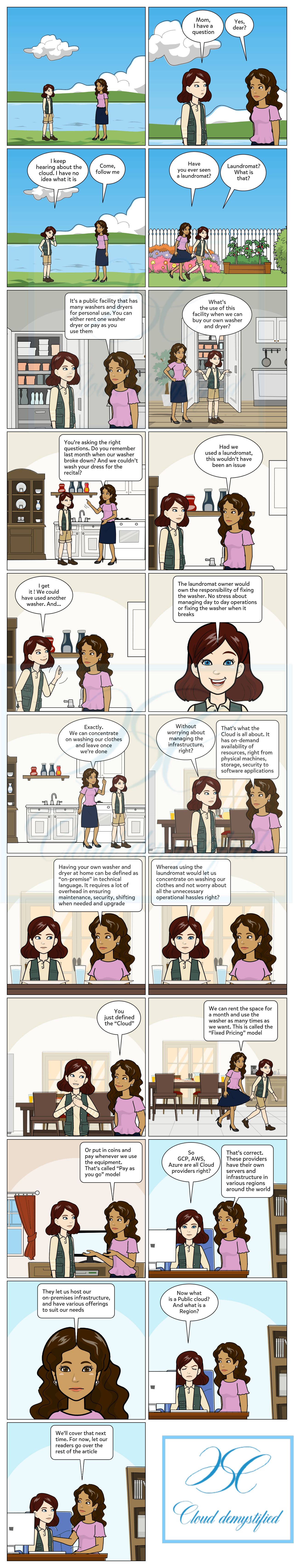
Have you ever wondered how several drops of water, dispersed across the earth come together at one place, in the form of a Cloud? If you have, then you’ve understood the core concept of Cloud Computing.
Cloud is a shared environment maintained by major providers where servers, networks, storage, development tools, and even applications are centrally hosted and enabled through the internet. Instead of organizations having to buy their own Hardware, train staff, and invest in ongoing maintenance, some or all of these needs are handled by a cloud service provider.
Benefits
Apart from not worrying about maintenance and operations of on premise infrastructure, Cloud providers also enable access with low latency and high availability, creative pay as you go pricing models, on demand self serviceability, multi tenancy model and elasticity.
Wait, too much to digest? Let’s take it one byte at a time.
Low Latency and High Availability
Have you ever logged into a website only to keep waiting for it to load, and finally see an error message? That’s exactly where Cloud providers come to the rescue. Low latency simply means the ability to process large volumes of data with minimal delay, and high availability is a design to avoid loss of service by reducing or managing failures.
Creative Pricing Models
This term is exactly what it sounds like. Organizations can decide if they want to pay for the services as they use them, or enrol in a subscription based payment.
Most Cloud providers have creative pricing models with sustained use discounts, where organizations can dynamically choose the pricing plan that works best for them.
On Demand Self Serviceability
Cloud Providers have made is easy for organizations to request and get resources (like VMs) provisioned at the blink of an eye, without having to go through tedious steps of manual setup and configuration.
Multi Tenancy Model
This term simply means “shared resource pooling”. Cloud has the provision of letting users share a single application, avoiding duplication and redundancy. Each user, called a “tenant” can reconfigure the resource according to their needs.
Elasticity
Have you ever stretched a rubber band to tie your hair or seal a packet of chips? That’s exactly what cloud providers enable us to do. An organization can scale its resource usage up or down rapidly with ease, as their needs change.
Security
Cloud providers have a robust security model, while ensuring encryption and compliance of the data. However, they use a shared responsibility model where users and the providers have to adopt best practices and stay vigilant to ensure high security standards.
I’ll dig deeper into each of these offerings in a later post
Cloud Providers
There are a few widely adopted, major public cloud provider such as GCP (Google Cloud Platform), Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, Microsoft Azure and Alibaba Cloud. However, the list of cloud and cloud service providers is huge, growing at the blink of an eye.
Redhat has compiled a list of Cloud service providers, accessible via their database:
https://redhat.secure.force.com/finder/
What Next?
As we’re navigating through a global pandemic, organizations are dynamically evolving and shifting their priorities to make data accessible and secure, while ensuring optimal utilization of money and resources. This has made it even more critical for professionals and organizations to adopt the Cloud, and deliver efficiency to the users.
So what are you waiting for? It’s time to reimagine, revolutionize and grow